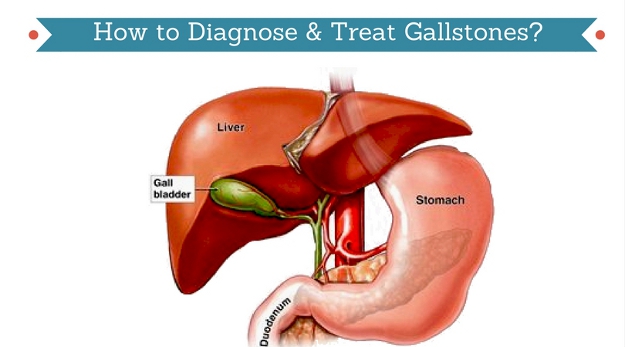
An introduction to gall stones
Gallbladder is a small pear shaped organ located on the right side of human body beneath the liver. It plays an important role in digestion by secreting a substance known as bile. Bile is responsible for digesting fats and vitamins A,D,E and K.
Due to this function of bile sometimes excess cholesterol gets stored inside the gallbladder leading to formation of tiny stones. Gall stones are mostly formed of cholesterol and in some instances they are formed of bilirubin. Bilirubin is a pigment formed by gallbladder which imparts the normal yellow colour to urine.
Causes of gall stones
Rather than specific causes, certain pre-disposing factors are more likely to cause gall stones. Some of the most common causes which lead to formation of gall stones are listed below:
Genetic structure:
Genes are responsible for deciding every aspect of human body and mind. If the gene responsible for gallbladder or bile function is faulty, it may pre-dispose a person to develop gall stones.
Age:
Gall stones are observed more commonly in adults who are in their 40s or above and less commonly in young adults or children. Females in their 40s are more likely to develop gall stones than men.
Diet:
A balanced and healthy diet is less likely to aid disease formation in any person. People who consume food with high fat content on a regular basis tend to have high cholesterol levels. This leads to more cholesterol available for digestion leading to cholesterol stones.
Weight:
People who are over weight or bordering towards obesity tend to have higher chance of developing gallstone as opposed to people whose weight is within normal limits.
People with any of these pre-disposing factors should remain cautious about their overall health and diet. If any symptoms of gall stones are felt a doctor should be consulted immediately.
Symptoms of gallstones
Gallstones are not a sudden development. They get formed gradually due to accumulation of excessive cholesterol or due to bilirubin sludge. Symptoms of gallstones are as follows:
Pain:
Pain is experienced in upper right side of abdomen. This is because the gall bladder gets irritated due to presence of stones. The pain maybe dull and constant most of the times. However, if there is sudden torsion of the gall bladder in an attempt to expel the stones, patient may experience sudden gripping pain in the abdomen. This is a medical emergency and patient must be taken to a hospital immediately.
Digestive troubles:
People who have gall stones often complain of a sensation of heaviness in the abdomen, poor digestion, excessive urge to burp often and acidity attacks repeatedly.
Silent gall stones: Some patients of gall stone do not exhibit any symptoms at all. Their condition may be an accidental discovery while performing investigations for some other health conditions.
Diagnosis of Gall Stones:
Gall stones have tendency to remain silent and not display any specific symptoms. Therefore they may tend to remain undiagnosed for a long time. Many a times gallstones are discovered accidentally while performing diagnostic procedures for other health disorders. But if a patient presents with symptoms of gall stones, they are usually asked to undergo the following investigations:
USG:
Sonography is the best diagnostic test which will detect gall stones. The test also reveals the number, location and dimension of stones thus indicating severity of the condition.
MRI:
MRI is a rather advanced investigative test and not required for a simple case of gall stones. However in complicated cases of gall stone where diagnosis is unclear, MRI may give a clearer picture and help the doctor understand his/her patient’s condition better.
ERCP:
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreaticography is a diagnostic as well as therapeutic technique. It helps in detecting gall stones that might have migrated from gallbladder into the bile duct. Such stones can be removed during the procedure itself.
Blood Tests:
Blood tests do not help in detecting gall stones. But they are helpful in detecting complications of gall stones like jaundice, pancreatic dysfunction, gall bladder inflammation etc.
Treatment of Gall Stones
Once results of diagnostic tests are obtained, doctors get a clear idea about the patient’s condition. Depending on the severity of gall stones, patient can undergo either of the following treatment methods:
Medical Therapy:
Medical management of symptoms like pain, acidity, slow digestion can be done for patients who are not being bothered a lot by their gall stones. Continuous monitoring of patients is required to assess their health condition.
Surgery:
Surgery is the ultimate solution for gall stones when medicines stop working effectively or when patient is experiencing symptoms of gall stones with great severity. Gall stones are surgically treated by removal of gall bladder. This results in reduced production of bile and biliary enzymes. People who undergo the surgery will never suffer from gall stones again. But there are a lot of dietary restrictions after gall bladder removal surgery. They have to be followed well in order to have successful outcome of the surgery.
Gall stones is not a life threatening condition if they are diagnosed on time and treated well. Patients are advised to be careful and observant of their health in order to avoid health complications due to gall stones. Early diagnosis and early treatment are the best options to keep oneself healthy.